These transactions can relate to assets, liabilities, equity, sales, expenses, gains, or losses – in essence, all of the transactions that are aggregated into the balance sheet and income statement. The ending balances in these accounts are then aggregated and reported in the balance sheet and income statement. The totals calculated in the general ledger are then entered into other key financial reports, notably the balance sheet — sometimes called the statement of financial position. The balance sheet records assets and liabilities, as well as the income statement, which shows revenues and expenses.
- Incidentally, Pacioli popularized the vernacular Venetian terms “debere” (to owe) and “credere” (to entrust), from which debit and credit accounts get their names.
- This ledger can also be used to keep track of items that reduce the number of total sales, like returns and outstanding amounts still owed.
- A ledger is where the most important information necessary to create financial statements is located.
- That means the financial information, as well as the more detailed journal entries that feed into it, provide a picture of the past.
- These articles and related content is not a substitute for the guidance of a lawyer (and especially for questions related to GDPR), tax, or compliance professional.
At times this can involve reviewing dozens of journal entries, but it is imperative to maintain reliably error-free and credible company financial statements. Double-entry transactions, called “journal entries,” are posted in two columns, with debit entries on the left and credit entries on the right, and the total of all debit and credit entries must balance. A company’s GL is the basis of its financial reporting and the source of the information used therein.
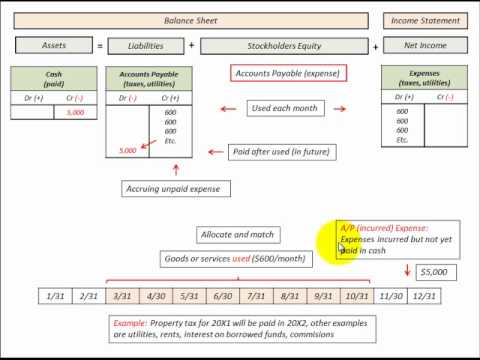
A Balance Sheet Transaction Example
Reconciliation involves checking each account within a general ledger to verify accuracy. The process begins by gathering the information for each account in review, then examining any journal entries which have been made to correct errors in the ledger. Combining machine learning enabled financial processes and real-time recording of transactions, traditional accounting functions such as closing the books can occur in a fraction of the time it used to. Accounts receivable (AR) refers to money that is owed to a company by its customers.
They are sometimes broken down into departments such as sales and service, and related expenses. The expense side of the income statement might be based on GL accounts for interest expenses and advertising expenses. A general ledger can have any number of subledgers, sometimes also known as journals. Some of the most common types of subledgers include accounts payable, accounts receivable, cash, assets, expenses, and income.
Policies & Reports
An accounting ledger, also commonly called a general ledger, is the main record of your business’s financial standing. It functions as the repository of all financial transactions and is used to prepare a number of reports, including balance sheets and income statements. A general ledger is an accounting record of all financial transactions in your business. This includes debits (money leaving your business) and credits (money coming into your business). These transactions can occur across areas such as revenue, expenses, assets and liabilities.
What is meant by general ledger accounting?
A general ledger, or GL, is a means for keeping record of a company's total financial accounts. Accounts typically recorded in a GL include: assets, liabilities, equity, expenses, and income or revenue.
In this instance, one asset account (cash) is increased by $200, while another asset account (accounts receivable) is reduced by $200. The net result is that both the increase and the decrease What Is A General Ledger Account? only affect one side of the accounting equation. If you look at the information that’s recorded in an accounting journal and an accounting ledger, a lot of it would look the same.
Why Use a General Ledger?
A company may opt to store its general ledger using blockchain technology, which can prevent fraudulent accounting transactions and preserve the ledger's data integrity. The income statement will also account for other expenses, such as selling, general and administrative expenses, depreciation, interest, and income taxes. The difference between these inflows and outflows is the company's net income for the reporting period. When a company receives payment from a client for the sale of a product, the cash received is tabulated in net sales along with the receipts from other sales and returns.
The chart is usually organized to show all balance sheet accounts, followed by all income statement accounts. Examples of other general ledger accounts that are commonly used are noted below. At the end of each fiscal period, a trial balance is calculated by listing all of the debit and credit accounts and their totals. Those with debit balances are separated from the ones with credit balances. The debit and credit accounts are then totaled to verify that the two are equal.
Join Sage
In that situation all of the detail that supports the summary amounts in one of the control accounts will be available in a subsidiary ledger. With modern accounting software, you may not have a purchase or sales ledger. Instead, they can be marked as a certain type of entry and called up in a search if you want to look at these entries on their own.

But there are some differences between how the two records function so it’s important to understand how they work together. In the event of an audit, balances on financial statements should link back to all of the posted transactions that make up that balance. These are typically recorded in the general ledger as they are incurred. Your general ledger might break these down https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/6-hacks-to-improve-your-working-capital-management/ into accounts for rent, merchant fees, software subscriptions, telephone and internet, cleaning, and so on. To maintain the accounting equation's net-zero difference, one asset account must increase while another decreases by the same amount. The new balance for the cash account, after the net change from the transaction, will then be reflected in the balance category.
For example, sales may be further divided into retail sales and wholesale sales, or foreign sales and domestic sales. Although there are many possible accounts in a general ledger, they can all usually be classified into permanent and temporary categories. Let’s look at some of the accounts small businesses may use in the general ledger. Here is an example of an accounting system transaction within a general ledger for a fictional account, ABCDEFGH Software. Instead, they show actual amounts spent or received and not merely projected in a budget. Use the general ledger report in QuickBooks to see a complete list of transactions from all accounts within a date range.
- However, a separate ledger for the company's accounts receivable will reflect a credit reduction for the same amount, because ABCDEFGH Software no longer has that amount receivable from its client.
- If discrepancies are found, reconciliation requires investigating for unusual transactions, or otherwise explaining the error.
- The income statement might include totals from general ledger accounts for cash, inventory and accounts receivable, which is money owed to the business.
- The transaction details contained in the general ledger are compiled and summarized at various levels to produce a trial balance, income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and many other financial reports.
This data from the trial balance is then used to create the company’s financial statements, such as its balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and other financial reports. A general ledger represents the record-keeping system for a company’s financial data, with debit and credit account records validated by a trial balance. It provides a record of each financial transaction that takes place during the life of an operating company and holds account information that is needed to prepare the company’s financial statements. Transaction data is segregated, by type, into accounts for assets, liabilities, owners’ equity, revenues, and expenses.
Why do businesses need general ledgers?
The accounts receivable process begins when a customer purchases goods or services from a company and is issued an invoice. The customer usually has a set amount of time to pay the invoice, such as 30 days. For this transaction, the credit column will remain unchanged for this account. However, a separate ledger for the company's accounts receivable will reflect a credit reduction for the same amount, because ABCDEFGH Software no longer has that amount receivable from its client. While the above accounts appear in every general ledger, other accounts may be used to track special categories, perform useful calculations and summarize groups of accounts. Other GL accounts summarize transactions for asset categories, such as physical plants and equipment, and liabilities, such as accounts payable, notes or loans.
- The general ledger can, for example, help a business find where increased expenses are coming from, and it allows a bookkeeper or accountant to search out and correct errors.
- Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years.
- If the accounting equation is not in balance, there may be a mistake in your journal entry.
- Whether each adds to or subtracts from an account's total depends on the type of account.
- When your business records revenue from sales, this will increase owner’s equity because it means that the company has earned more money.
- “A general ledger (GL) is a parent copy of all the financial transactions of a business.

Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.